Micro and Ultrafine Bubble Generation
What makes Ultra-Oxygen bubbles so special?
Micro and Ultrafine bubbles generated with the patented equipment of Ultra-Oxygen, are not your ordinary bubbles. These tiny, charged bubbles possess remarkable properties that set them apart from their larger counterparts. Ultrafine bubbles are so small that they measure under 50 microns and can even shrink naturally down to 350 nanometres. These bubbles are incredibly stable, neutrally buoyant, and can remain suspended in water for months.
Ultrafine bubbles are not just any bubbles; they have a charged surface that can perform electrochemistry and oxidative reactions. With the right mixture of iron and oxygen molecules, these bubbles can do oxidation reactions, making them ideal for a variety of applications.
These tiny bubbles also have the ability to reduce surface tension and pH of water, creating amazing effects in the water. This unique class of bubbles has even gained a new classification under ISO/TC 281 – Fine bubble technology.
Ultrafine bubbles are truly a superior aeration technology that can efficiently aerate the entire water column. With all these fascinating benefits, it is no wonder that ultrafine bubbles are a game-changer in many industries.


How superior are Ultra-Oxygen Micro and Ultrafine bubble generators? (MB/UFB)
The major benefits users recorded, studies verified, and results obtained from using MB/UFB aeration equipment can be summarized as follows:
- Ability to replace lost oxygen in water bodies very fast and efficiently, to use other gasses such as ozone more efficiently in water treatment processes, and to supersaturate water with oxygen up +- 450% – 38mg/L.
- Eliminate up to 70% to 90% of algae, reduce chlorophyll by 50%, and remove 80% to 100% of Manganese, Iron, Hydrogen Sulphide, and Copper Sulphate in water by oxidation.
- Prevent the occurrence of toxic blue-green algae.
- Increase agriculture productivity and control fouling in sand filters and clarifiers.
- Prevent biofouling growth and safe for fish, plants, and other aquatic life.
- Reduce and prevent taste and odour problems, improve water quality, and reduce pH, TSS, BOD and chemical dosage.
- Remove surfactants, enabling Lower cost to treat wastewater (less CAPEX and OPEX),
- Increased treatment capacity of WWTP and makes smaller process units & ancillary equipment more efficient to improve water quality.
- Improved energy efficiency to treat water and improve BOD / COD / N removal efficiencies.
- Less chemical usage and prevent clogging of filters.
- Improve coagulation and flocculation processes.
- Lower bacterial counts, reduce the risk of spreading legionella, Improve habitat for fish, and wildlife, and increase Aesthetic Appearances.
- Reduce chemical expenses and improve Yield and Quality of crops, and the health of all species that live in water and create a healthier environment that promotes the well-being of humans.
HOW TO START TO IMPLEMENT MB/UFB AERATION?
The first step in designing an aeration system is to determine the oxygen demand. Although process model simulations aid in determining oxygen demand and aeration requirements, it is important to understand the factors that influence oxygen demand and how oxygen demand is calculated.
Connect the pump that will provide the recommended water flow at the recommended pressure.
Water that flows through the system will automatically pull in air or gas into the system and mix it with the water and produce micro and ultrafine bubbles.
The bubble sizes can be changed via the air/gas intake lines. Consult with your local UO2 specialist for more information to ensure you are aware of what will influence air intake performances.
Establishing the correct flow and load criteria is imperative to the success of the aeration system design. Design guidelines recommend accounting for the 24-hour demand of the average day of the peak month when calculating the maximum aeration requirements.
The Four Musketeers
- OXYGEN (The Boss) – You must know how much Oxygen (not air) is needed to treat the water.
- VOLUME – You must know how much volume of water must be treated.
- TIME – You must know how much time you have to dissolve the OXYGEN in the VOLUME of water received.
- QUALITY – You must know the quality requirements your discharge water must adhere to before discharging it.
DISSOLVED OXYGEN’S IMPORTANCE
What’s dissolved oxygen (DO)?
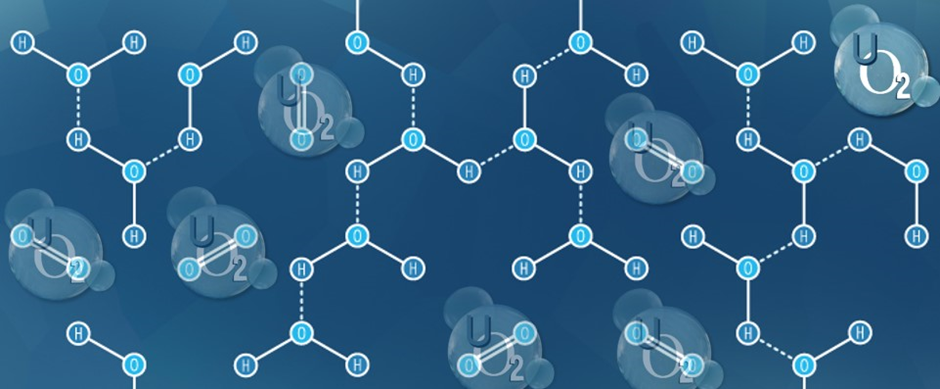
The bonded oxygen molecule in water (H2O) is in a compound and does not count toward dissolved oxygen levels. One can imagine that free oxygen molecules dissolve in water much the way salt or sugar does when it is stirred.
Once dissolved in water, it is available for use by fish, invertebrates, aquatic plants, plants, animals, good bacteria, and all other living organisms. DO plays a significant role in many chemical processes in the aquatic environment and is considered the most important measure of water quality as it is a direct indicator of an aquatic resource’s ability to support aquatic life.
Microbes such as bacteria and fungi require dissolved oxygen (DO) to decompose organic material in water. Microbial decomposition is a crucial contributor to nutrient recycling and if there is an excess of pollution and decaying organic material (from dying algae and other organisms), the oxygen levels will get used up quickly.
Anaerobic conditions then occur when the uptake or disappearance of oxygen is greater than its production by photosynthesis, diffusion, or aeration. Many anaerobic bacteria produce enzymes that destroy tissue or sometimes release potent toxins.
The only way to restore nature in this state is to add oxygen back to the water, and here lies the challenge.
Normal aeration bubbles only contain 21% oxygen, rise too fast and require a high energy source to transfer enough oxygen to restore the water in an aerobic condition.
Ultra-Oxygen Micro and Ultrafine bubble-generating technology solved this problem by creating bubbles that rise very slowly and can stay in water for months if not used. This allows the use of oxygen generators that produce up to 93% oxygen efficiently for the first time in the history of aeration.
Dissolved oxygen is usually reported in milligrams per litre (mg/L), as a percentage (%) of air saturation, or in parts per million (ppm). 1 mg/L is equal to 1 ppm.
Dissolved oxygen is an essential factor for the activity of microbial biocatalysts used in enhanced bioremediation, as it is a key component for aerobic respiration, the primary metabolic pathway for many microorganisms.
During aerobic respiration, microorganisms use oxygen to break down organic compounds into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. This process releases energy that can be used to fuel microbial growth and metabolism. In the context of bioremediation, microorganisms use this process to break down contaminants in contaminated environments such as soil or water.
The presence of dissolved oxygen in the environment promotes the growth and activity of aerobic microorganisms that can degrade pollutants, such as hydrocarbons and other organic compounds, more efficiently than anaerobic microorganisms. By providing sufficient dissolved oxygen, the bioremediation process can be accelerated, allowing for faster and more complete removal of contaminants from the environment.
Therefore, the availability of dissolved oxygen is critical for the activity of aerobic microorganisms and the success of enhanced bioremediation techniques that rely on these microorganisms as biocatalysts. In situations where dissolved oxygen is limited, alternative remediation approaches may need to be considered, such as anaerobic bioremediation or the use of other non-biological remediation methods.
Ultra-Oxygen micro and ultrafine bubble (MB/UFB) generators transfer more oxygen into the water compared to conventional aeration techniques, creating a more oxygen-rich environment that can enhance the activity of aerobic microorganisms involved in bioremediation. This increased oxygen supply helps to improve the metabolic activity of microorganisms, promoting their growth and increasing their biocatalytic efficiency.
Using MB/UFB technology also helps to reduce the toxicity of pollutants by promoting the biodegradation of contaminants into less harmful compounds. This can be particularly important for the bioremediation of organic pollutants, such as petroleum hydrocarbons, where UFBs can enhance the activity of aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms involved in the degradation process.
Overall, the use of MB/UFBs in microbial biocatalysts for enhanced bioremediation can help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the bioremediation process, making it a promising technology for the treatment of contaminated water and soil.
Ultra-Oxygen dissolved oxygen meters, sensors, and water monitoring equipment can be used to monitor water quality parameters.
We believe, “If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it.”, and strongly recommend the use of technology to manage the elements that promote water quality.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION & INSTRUCTIONS
General
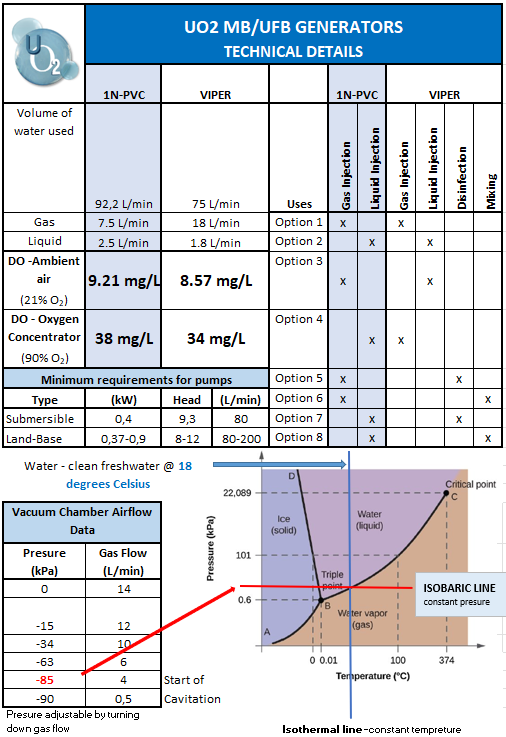
The UO2 MB/UFB generators are manufactured with high-quality PVC materials that can withstand a maximum of 4-9 bar pressure. It is however recommended to use 4 bar pressure at most to enhance product lifetime.
The client must do the needed tests to ensure that pressure losses are taken into consideration to ensure the MB/UFB generators receive the needed mass flow, pressure, and pressure differential.
Pipes used for construction – ISO FLOW SANS 966 Class 9 to 12 uPVC.
Use liquids that are fluid and avoid high-viscosity liquids.
Use water that does not contain solids that can block the water flow through the units. The Viper-30 and Viper-100 can handle particles as big as 8mm and the 1N-Viper and 1N-PVC up to 4mm. Screens at intakes are required to ensure hard COD and BOD particles are prohibited from entering the equipment.
Consult your UO2 specialist if you are in doubt. (Pre-filtration screening of 3mm is recommended.)
Performance and testing
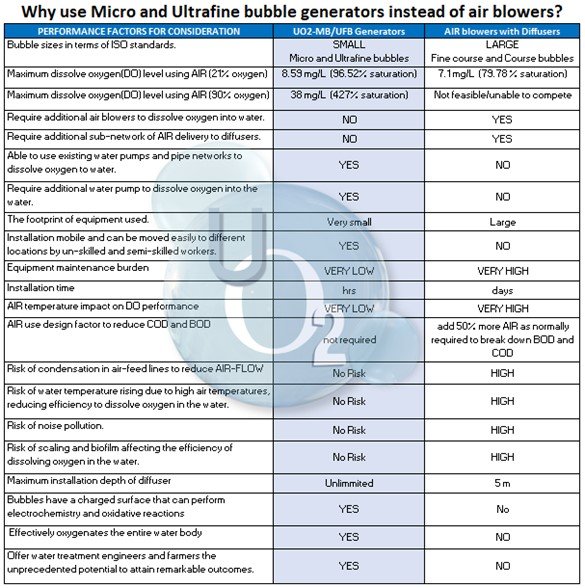
From the results, we ascertained that for wastewater treatment where a constant 2-3 mg/L is required the UO2-MB/UFB generators outperformed normal disk and strip diffusers by far.
Technical data obtained from various commonly used air diffuser manufacturers revealed that the actual oxygen transfer efficiency ranged between 1% – 2% whereas the UO2-MB/UFB generator can dissolve gas at a rate of 50 to 215% and can use up to 72 times less air to do the same job efficiently.
UO2-MB/UFB generators, when using an oxygen concentrator that provided 90% oxygen in the air bubbles could dissolve the oxygen in the 400 L of water at a rate of 0.038 mg/sec, a phenomenal 442 % increase in efficiency when compared to using ambient air.
A brief explanation of how the VIPER30 and 100 MB/UFB generators work:
The VIPER MB/UFB generator is NOT A VENTURI and was designed to complement the 1N-PVC MB/UFB generators; after discovering that surplus pressure energy from the motive, fluid was available. This additional energy was used to design a solution able to multitask like no other aeration solution in the world.
Combining the functions of an ejector, injector, jet pump, vacuum generator, and venturi enabled the UO2-Viper to generate micro- and ultrafine bubbles, to add gas in a liquid, to add a liquid to a liquid, to use cavitation to assist with disinfection, and to improve the quality of mixing in of nutrients in the water.
Water flows into the UO2-Viper at a higher pressure than it exits. This pressure difference creates a vacuum at the suction port on the side of the device. This sucks air, oxygen, ozone, or liquid into the main water stream. So, the more significant the pressure difference, the greater the vacuum and, with that, the greater the mixing efficiency.
What makes the UO2-Viper unique is that in venturis, gas and liquid are pulled, via a hole unevenly, into a single mixing vortex, whereas in the Viper’s case, the gas or liquid is received by a large suction chamber and feeds this evenly via the perimeter of the water jet and entrance hole of the diffuser that leads through to the diverging cone.
In the VIPER, the static pressures in the suction and mixing zone chambers can be decreased below the vapour pressure by as much as -90 kPa at a constant flow of water by reducing the airflow to the suction chamber, allowing water to evaporate in the formation of bubbles (Vapor bubble grows at low pressure). It collapses within milliseconds in a spectacular physical event as it is transported with the flow from where it was formed at low pressure to areas with higher pressure. The bubble will stop growing when local pressure exceeds vapour pressure, and because liquid water occupies many thousand times less volume than vapour, the bubble implodes.
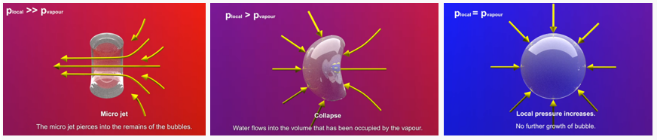
Also known as cavitation, the water is forced to become water vapour by the physical creation of micro vacuums “bubbles” underwater. These “bubbles” are made of water vapour only. No air or gasses are involved. These “bubbles” entirely collapse to form liquid water again. The jet velocity can reach up to hundreds of m/s.
It must be noted that cavitation does not increase DO levels in the water. However, due to the ability to create a negative pressure up to -90 kPa in the suction chamber, the Viper MB/UFB generator can raise DO levels and use Cavitation simultaneously in water with a temperature of 10 degrees Celsius.
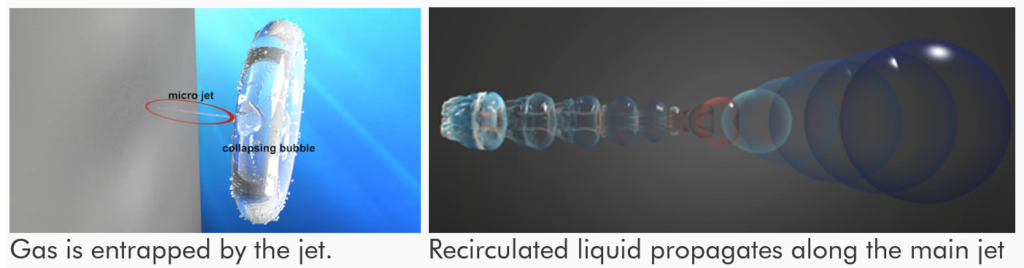
In general, cavitation is one of the elements of an integrated treatment system consisting of physical, chemical, and biological processes.
The effects of cavitation have become very useful in supporting chemical processes in environmental protection technologies, especially in technologies related to the decomposition of substances particularly harmful to humans and their immediate surroundings.
Benefits expected from 1N-PVC and VIPER-30 combination
(1N-VIPER)
It improves coagulation and flocculation, drops zeta potential, increases oxidation potential that helps to remove bacteria and parasites, raptures their cell walls, and then kills them by oxidation.
It increases the biodegradability of organic compounds in polluted water—and exhibits bactericidal activity during water treatment.
Decrease the amount of persistent organic pollutants in wastewater treatment plant effluent. Biological disinfection of water.
- The ability to mix 2 different liquids in a liquid simultaneously.
- The ability to mix liquids and gasses simultaneously.
- The ability to use the unit as a dozing pump.
- The ability to use the unit as a diffuser and mixer.
- The system is an easy plug-play system.
The 1N-VIPER on one pump can, therefore, do the following:
WARRANTY
The unit comes with a 1-year warranty subject to registering your project and equipment utilization with Soldevco Pty Ltd, adhering to their terms and conditions, and fair wear and tear.
Visually the unit may show some glue marks, but that is normal. We focused first on performance, price, and lastly looks.
The primary purpose of the equipment is to raise and maintain Dissolved Oxygen (DO) levels in water and to use the benefits of cavitation for mixing and disinfection purposes. Consult the manufacturer prior to using the equipment for any other purposes before use.
Although the maximum DO level achieved in clean fresh water with an oxygen concentrator (using +- 90% oxygen) was 28 mg/L, and with ambient air (using +- 20 % oxygen) was 8,57mg/L at a temperature of 18,5 degrees Celsius, we recommend that site-specific conditions be considered in your project designs.
The level of oxygenation required, the volume of water, and time to achieve the necessary level of Dissolved Oxygen, and the volume of water stored in reservoirs, will determine the type and quantity of MB/UFB units required. Therefore, site-specific engineering is recommended to determine the most effective solution for each project.
CLOSE-OUT COMMENTS
Oxygen and Micro and Ultrafine bubbles are necessary elements in all forms of life. The level of dissolved oxygen (DO) is one of the best indicators of overall water quality.
UO2-MB/UFB generators are the world’s best-priced, most cost-effective, sustainable, robust, easy to use, and the most environmentally friendly way to create Micro- and Ultrafine bubbles smaller than 100 microns.
“It is crucial for humans to manage oxygen in the water to save our planet’s blue gold.”






